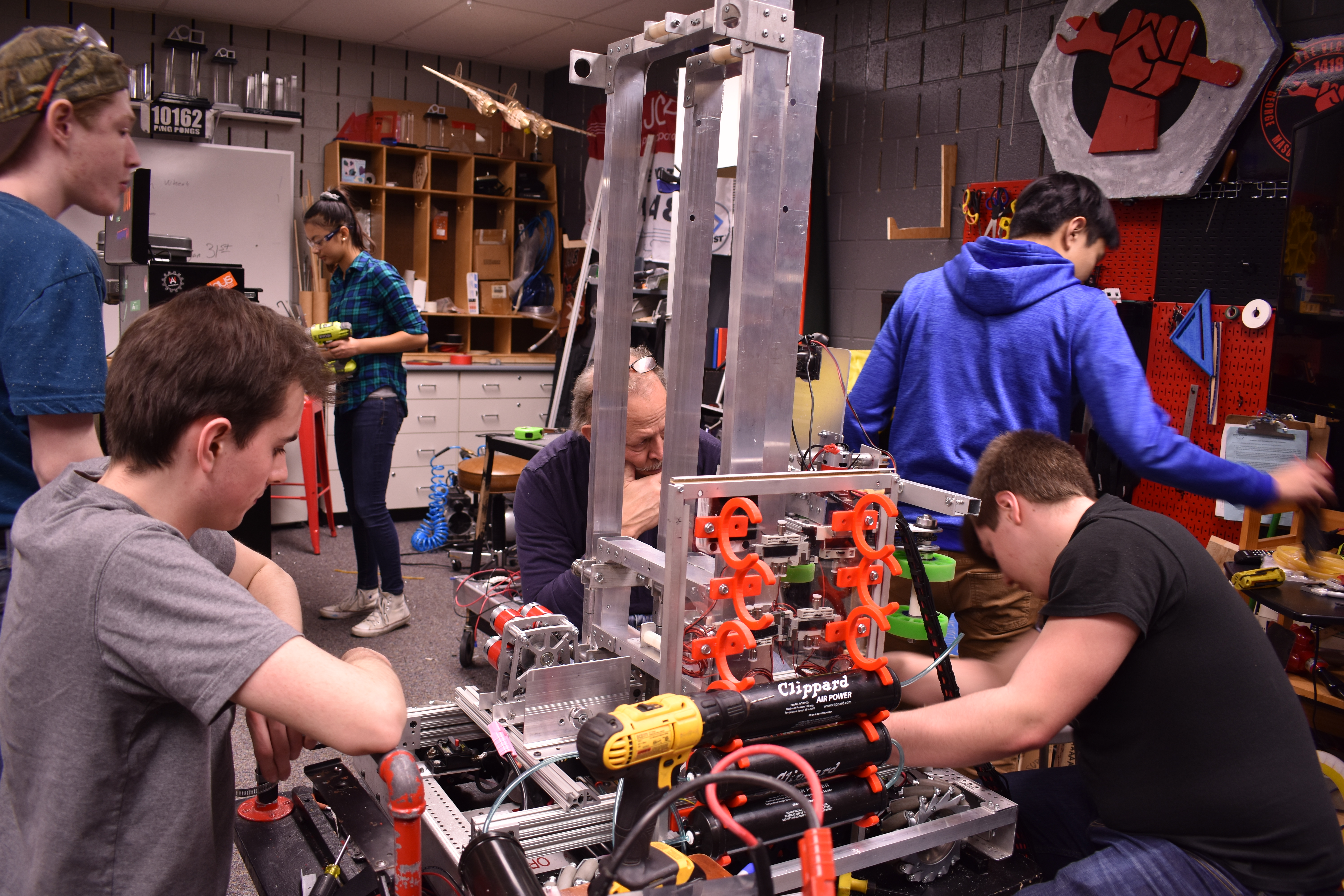
2019 Robot
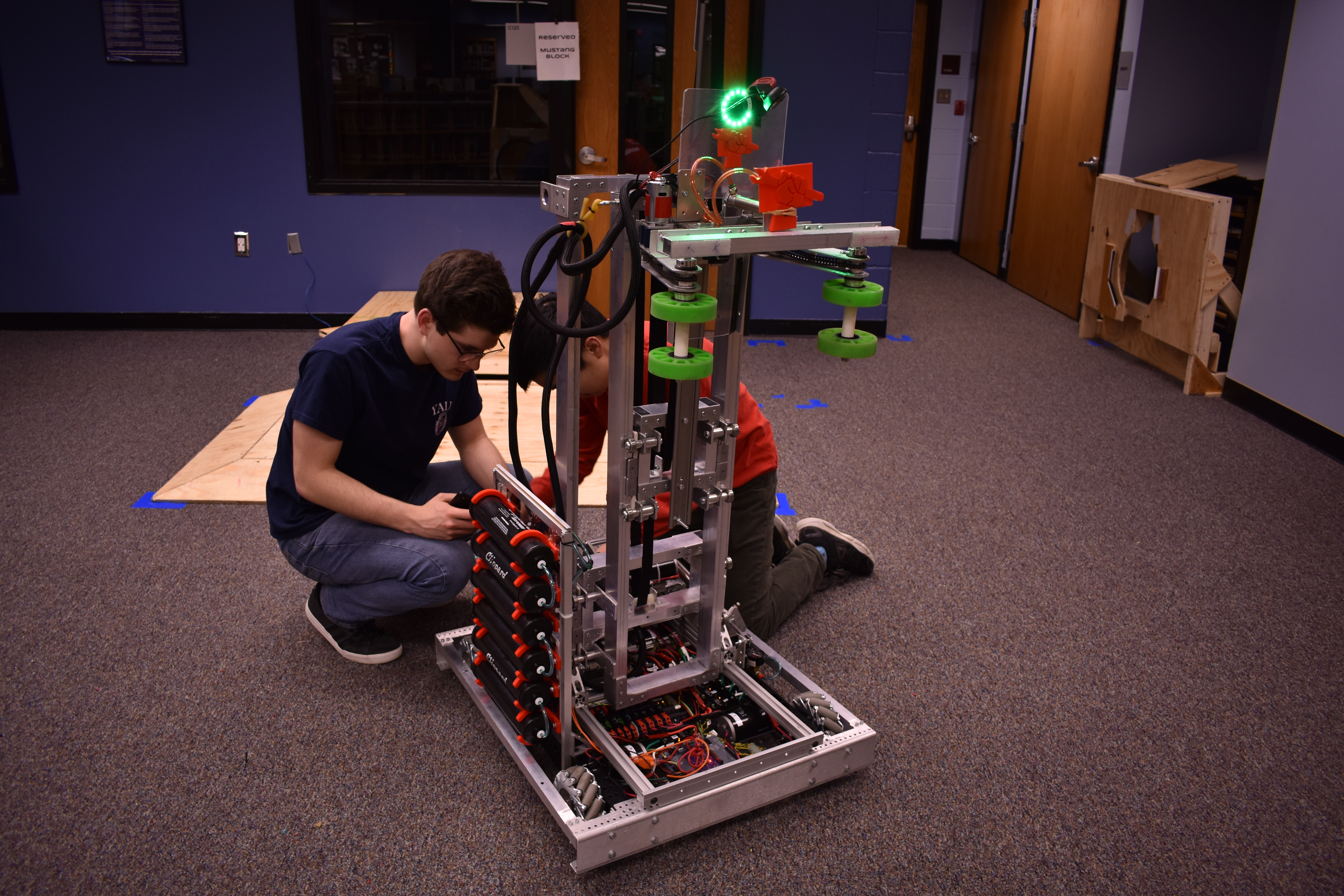
- Height: 1.5
- Height (extended): 3
- Width: 0.7
- Length: 1.02
Units:
The 2019 game's throwback to the Apollo 11 landing 50 years before provides a certain challenge for our team. It involves placing large balls and hatches into different locations on the field. To get a more detailed description of the game, see the official video reveal.
Robot Abilities
- Drive Train: Our 2019 robot uses mecanum drive to allow for high maneuverability. The ability to strafe allows us to line up with field elements quickly and easily, enabling fast cycling of both hatches and cargo. Our wheels are connected to a pair of Andymark Nanotube transmissions.
- Elevator System: Our elevator is based on a highly modified Andymark kit. The three stages allow us to reach all parts of the rocket. The elevator is driven by a single CIM motor connected to a Tough Box transmission, powering a set of pulleys.
- Cargo Intake: On the front of the elevator system lies a hinged arm with powered wheels which is used to collect and deliver cargo.
- Hatch Delivery: Placed directly on top of the cargo instake system, a pair of pneumatic driven fingers allow us to collect hatches.
- Winch: Utilizing a massive speed reduction gearbox, our robot has the capabillity to reach the top of the rocket.
- Climber Pistons: Our climbing mechanism consists of two pairs of pistons, located in the front and back of the robot. The first set lifts the front of the robot up, allowing us to drive forward onto the second level. The second set of pistons lifts the rear of the robot up, allowing us to drive forward onto the hab. All four pistons are capped by plastic wheels, allowing us to drive with either the front or the back extended.
Programming
Just like in previous years, we used Python for our robot code. In addition to our robot code, we developed a dashboard for our touchscreen driver station. It is written in JavaScript/HTML/CSS, and communicates with the robot through a python-based tornado server. It is based on the FRCDashboard framework we developed in 2016.
We drive using a pilot-copilot operating system, with one driver controlling robot motion and the other controlling all other robot functions. This allows each driver to control their own independent task, making operating the robot more efficient.
- Vision Software: With vision tape on the rocket and cargo ship, good vision software is very important to this challenge. Programmed in Python, this software uses data from a camera located on the elevator system and lots of math to position the robot correctly. There is also a button on one of the joysticks that runs the software in order to ensure the robot is perfectly lined up in TeleOp.
As usual, our code is open source, and can be found on our GitHub organization. Here are some quick links:
Competition Performance
We will be competing in two competitions this year at Battlefield HS (March 1-3) and at Oxon Hill HS (March 22-24). You can find out more about our competition performance and schedule on our Blue Alliance page, and look out for videos about our competitions on our YouTube page.






 2019
2019